Amazon Web Services announces new quantum computing chip

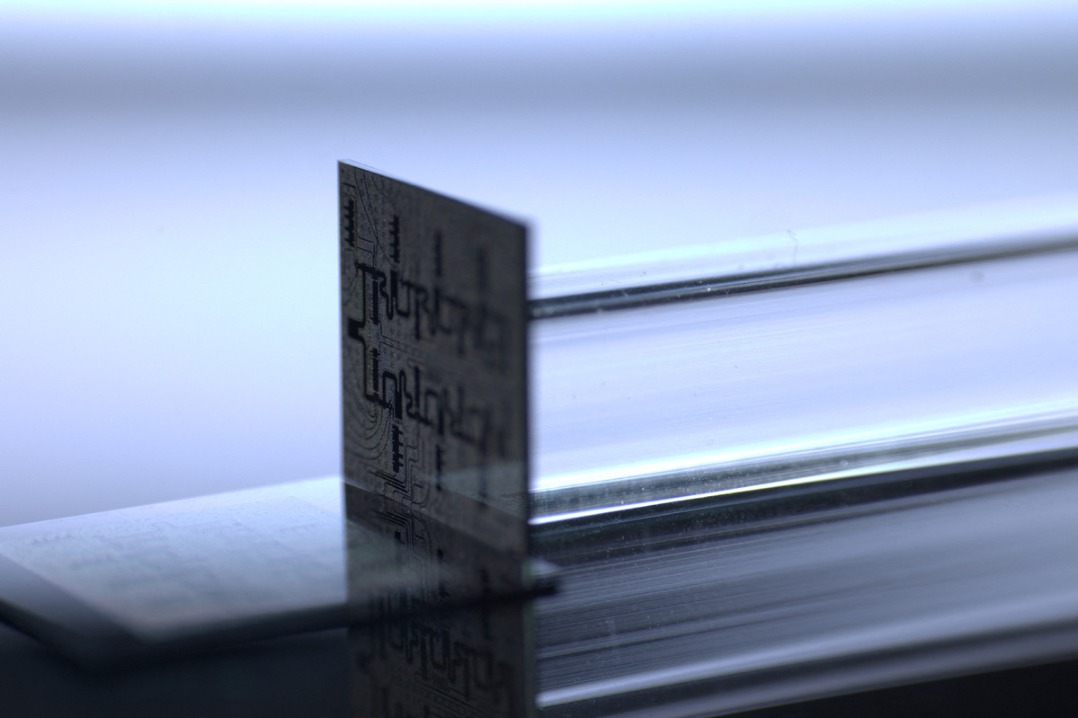
SAN FRANCISCO -- Amazon Web Services (AWS) on Thursday announced Ocelot, a new quantum computing chip that can reduce the costs of implementing quantum error correction by up to 90 percent, compared to current approaches.
Developed by the team at the AWS Center for Quantum Computing at the California Institute of Technology, Ocelot represents a breakthrough in the pursuit to build fault-tolerant quantum computers capable of solving problems of commercial and scientific importance that are beyond the reach of today's conventional computers, the company said.
AWS used a novel design for Ocelot's architecture, building error correction in from the ground up and using the "cat qubit". Cat qubits -- named after the famous Schr?dinger's cat thought experiment -- intrinsically suppress certain forms of errors, reducing the resources required for quantum error correction, the company said.
AWS researchers have combined cat qubit technology and additional quantum error correction components for the first time onto a microchip that can be manufactured in a scalable fashion using processes borrowed from the microelectronics industry.
"Today's announcement represents an important step in developing efficient means to scaling up to practical, fault-tolerant quantum computers," the company added.
"With the recent advancements in quantum research, it is no longer a matter of if, but when practical, fault-tolerant quantum computers will be available for real-world applications. Ocelot is an important step on that journey," said Oskar Painter, AWS director of Quantum Hardware.
AWS researchers have published their findings in a peer-reviewed research paper in Nature.
One of the biggest challenges with quantum computers is that they're incredibly sensitive to the smallest changes, or "noise" in their environment. To address the current problems associated with quantum error correction, Ocelot was designed from the ground up with error correction "built in."
"We didn't take an existing architecture and then try to incorporate error correction afterwards. We selected our qubit and architecture with quantum error correction as the top requirement. We believe that if we're going to make practical quantum computers, quantum error correction needs to come first," said Painter.
The team estimates that scaling Ocelot to a "fully-fledged quantum computer capable of transformative societal impact would require as little as one-tenth of the resources associated with standard quantum error correcting approaches," according to Painter.
He noted that as a promising start, Ocelot is still a prototype and AWS is committed to continuing to invest in quantum research and refining its approach.