CRCC subsidiary full steam ahead on transportation project


With recent COVID-19 resurgences coming under better control nationwide, State-owned builders are stepping up efforts in infrastructure, a move outlined in the nation's 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-25), to shore up livelihoods and the economy.
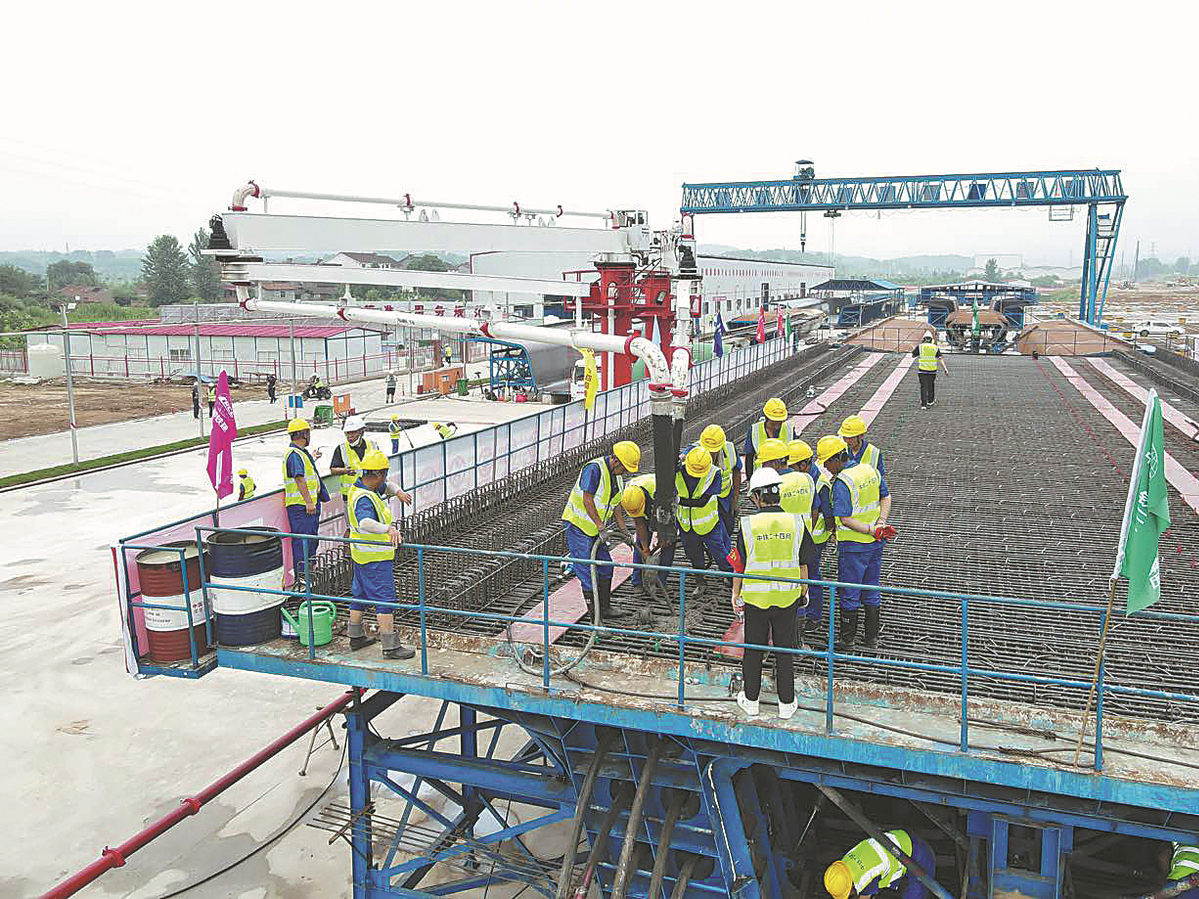
With the first box girder of the Wuyi section of the Shanghai-Chongqing-Chengdu high-speed railway readied recently, construction of the railway, a key livelihood project, has embarked on a new journey ahead of the final operation.
The Wuyi section, with a total length of 51.87 kilometers, was constructed by China Railway 24th Bureau Group Corp Ltd, a unit of China Railway Construction Corp, the nation's largest contractor.
There are 27 bridges planned in the project, which have a total length of 37.7 km and six tunnels at 6.4 km, including the 1,353-meter Dangyang tunnel, which became a "hard nut to crack" throughout the whole construction project.
Though faced with many difficulties, such as handling crossings with other railway lines, the builders have solved problems with various solutions based on on-site research and corresponding planning.
"Digging through the 1,353-meter-long tunnel is indeed a great success for us," said Qin Bing, a project manager with CR24. "But we have achieved more in the construction."
A key supporting facility of the project, the Dangyang beam fabricating yard, covering an area of 145 mu (9.7 hectares), was built in Yichang, Hubei province. It undertakes the prefabrication and erection of 526 box beams of the Wuyi section of the Shanghai-Chongqing-Chengdu high-speed railway, with a total construction period of almost two years.
The beam fabricating yard has boosted construction efficiency, as the facility is supported by concrete mixing stations, automatic vehicle washing platforms, wastewater treatment facilities and real-time noise monitoring. The yard can build as many as 60 box beams per month, with a maximum storage capacity of 94 box beams.
The SOE has handled environmental protection as one of the top priorities during the construction process. Qin said the construction team has built along the railway many other "small projects" to protect the environment, such as sewage treatment plants, a machinery washing platform and a cement stirring facility-all achieved using green operations.
"Environmental protection has been a buzzword in the Yangtze River development in recent years, and we have been going the whole hog to guarantee safe and environmentally harmless construction since the project started," Qin said.
With a designed speed of 350 km per hour, the operation of the project will have high-speed railway trains steaming ahead to more cities along the Yangtze River, boosting the development pace of the area and promoting the livelihoods of residents, the manager said.
Amid uncertainties from abroad and disruptions by the COVID-19 pandemic, increased efforts in infrastructure are even more important, considering its role in pulling in investments, expanding domestic demand and facilitating industrial chains, Cai Tongjuan, a researcher at the Chongyang Institute for Financial Studies at the Renmin University of China in Beijing, was quoted by Xinhua as saying.
Looking ahead, the nation should have a broader view about bringing more high-tech solutions into traditional infrastructure to accelerate upgrades in the sector, and also ramp up efforts in the "new infrastructure" to have the sector better serve the development of the real economy, Cai said.