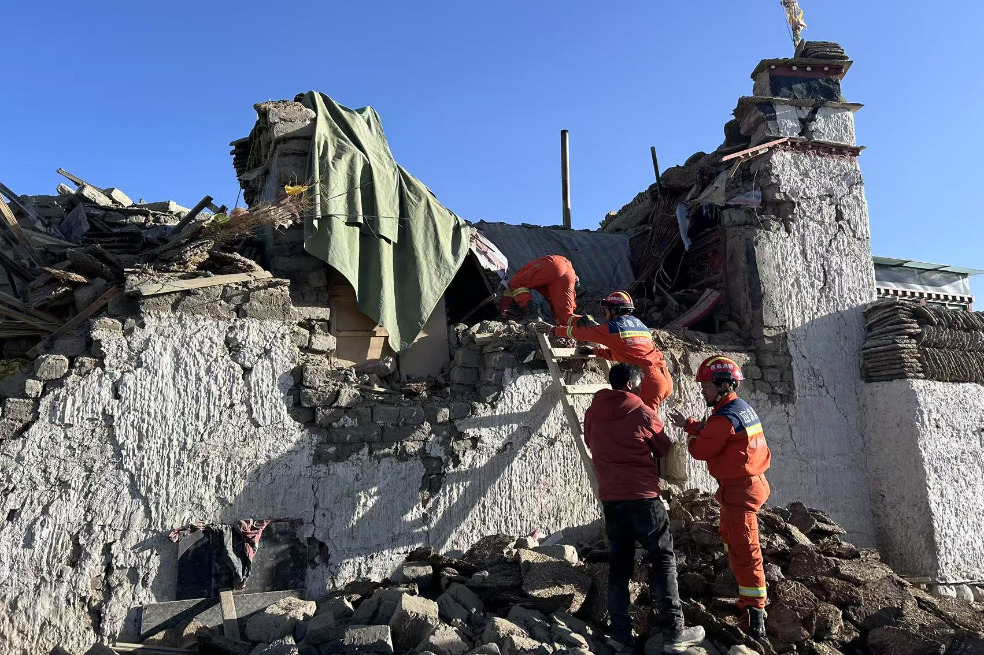
A creature that has served us well


Implications
For thousands of years, ancient China depended on an agricultural civilization and a corresponding small-scale peasant economy, in which cattle played an indispensable role, as was accentuated by experts in folklore studies including Wu Bing'an and Wu Yucheng.
According to Wu Yucheng, who is a council member at the China Folklore Society, early proof of the relationship between agriculture and the bovine species in China comes from the Hemudu site in Zhejiang province that dates back approximately 7,000 years. There paddy seeds, fossils of buffalo skulls, and farming tools made from buffalo bones were found.
The widely acknowledged academic view is that plowing with oxen became common during the Warring States Period (475-221 BC). Since then, the ox has evolved into a symbol of production and a supportive sidekick in everyday life.
In the renowned folk tale The Cowherd and the Weaver Girl, based on ancient stargazing, the girl, a deity responsible for weaving iridescence onto the sky, descends to the mortal world. There she marries a peasant boy owning only one ox-as a vignette, in some versions, the ox leads the boy to the girl as a gesture of gratitude.
They are then discovered by the superior gods and separated by the Milky Way. Moved by their tragic story, magpies form a bridge allowing them to see each other on the seventh day of the seventh lunar month, hence the provenance of Chinese Valentine's Day, or qixi.
Apart from honoring love, the folktale also represents an idyllic ideal for a household in ancient society-the men plowing the fields and the women weaving cloth, ensuring both food and clothing.