Scientists hit back against tidal wave of microplastics
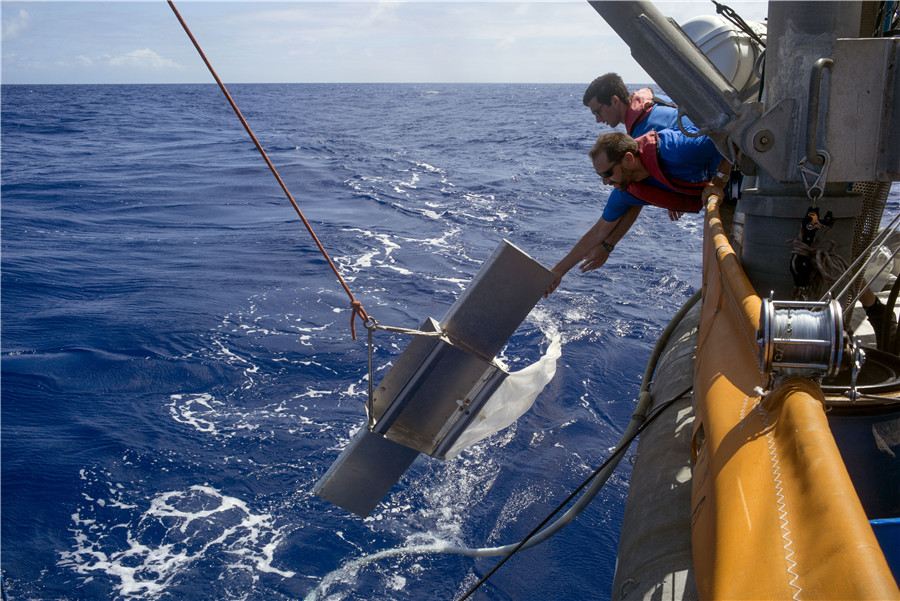


Stopping problem at source will be key to success, experts say. Xing Yi reports from Shanghai.
When marine biologist Edward Carpenter was on a research cruise in the North Atlantic Ocean's Sargasso Sea in 1971, he discovered plastic particles floating amid the seaweed in concentrations averaging 3,500 pieces per square kilometer.
The following year, Carpenter published the first observations of what are now known as microplastics in the journal Science. He noted, "increasing production of plastics, combined with present waste-disposal practices, will undoubtedly lead to increases in the concentration of these particles".
His prediction was correct, but it caused little concern until an increasing amount of evidence turned up over the past decade illustrating that microplastics have spread across the oceans, threatening marine life and humans alike.
At a national academic conference on microplastics pollution and control in Nanjing, Jiangsu province, on June 5 and 6, more than 500 scholars presented their findings and discussed the issue ahead of World Oceans Day on June 8.
Researchers define microplastics as particles with diameters ranging from less than 5 millimeters, about the size of a grain of rice, to just a few microns, about one-hundredth the diameter of a human hair.
To better identify sources, microplastics are divided into two categories based on their formation process - primary and secondary. The former are plastics that are inherently small, such as industrial scrubbers used to blast surfaces clean, plastic powders used in moldings, and micro beads found in cosmetics, toothpaste and facial wash.
Secondary microplastics are produced by the fragmentation and weathering of larger items, such as plastic fibers shed from synthetic clothing, small pieces of nets and foam boxes in the fishing industry, and plastic litter on beaches. Though plastic decomposes slowly, it ages under sunlight before breaking down into ever-smaller pieces in the natural environment.
"Almost all the plastic waste in our daily lives will eventually turn into microplastics," said Pan Xiangliang, director of the Environmental Microplastics Pollution Research Center at Zhejiang University of Technology in Hangzhou, capital of Zhejiang province.