US marriage ruling resonates in China
 |
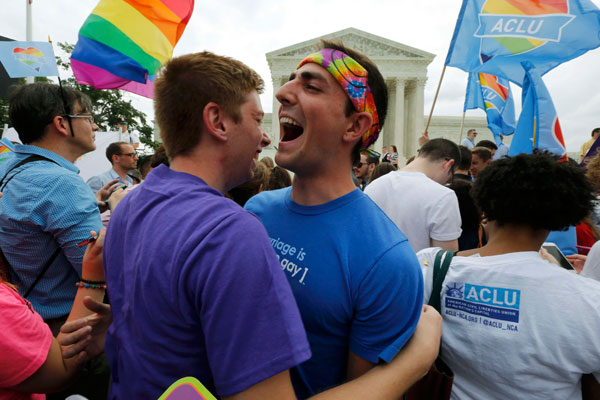
| Gay rights supporters celebrate after the US Supreme Court ruled that the US Constitution provides same-sex couples the right to marry, outside the Supreme Court building in Washington, June 26, 2015.[Photo/Agencies] |
The US Supreme Court 5-4 ruling on June 26 that same-sex marriages are protected under the 14th amendment of the US Constitution was a landmark judgment not only for Americans but also many Chinese.
The ruling means that same-sex marriage is legal in all US states, instead of the 37 before last Friday. But stubborn opposition to same-sex marriage in states such as Texas, Alabama and Kentucky means there are still battles ahead.
Americans have come a long way on this front. The Stonewall Inn in New York stands as a testament of the 1969 riots by the LGBT (lesbians, gays, bisexuals and transgender) community following a police raid of the bar.
When I spent a year in Honolulu between 1993 and 1994, people in Hawaii were fighting to make their state the first in the US to legalize same-sex marriage. The Crossroads Church across the street from the University of Hawaii at Manoa voiced their support. As a young Chinese journalist, I interviewed the president of the then Hawaii Gay and Lesbian Rights Association. However, it took Hawaii two decades to finally legalize same-sex marriage in December 2013.
It was already late at night in China when the US Supreme Court made the announcement. Yet many of my friends posted messages on the WeChat platform applauding the decision. Some quoted US President Barack Obama's words that "love is love," while others were amused to hear Justice Anthony Kennedy who referenced Confucius' writing that "marriage lies at the foundation of government."
Some Chinese felt proud that Confucius' teaching was used in making this historic decision. Others expressed doubt about the true meaning of Confucius words. Fang Zhouzi, a popular science blogger, believes the English translation was wrong. Some opposing same-sex marriage have quoted Confucius as saying that there are three kinds of unfilial conduct, the worst being having no descendants.
Li Yinhe, a famous sociologist and sexologist who has long advocated for gay and lesbian rights in China and a lesbian herself, believes China also has to fight discrimination against its LGBT community.
While substantial progress has been made in China over the past two decades to protect the rights of the LGBT community, most Chinese are still not ready to embrace the group.
On April 25, a job fair in my hometown Shanghai for the LGBT community drew only 17 of the 150 companies invited. Unofficial statistics suggest that there are 30 million gays and lesbians aged 15 to 60 in China, most still living underground.
As a prelude to the US Supreme Court decision, seven gay and lesbian couples from China held a group wedding in West Hollywood, California, on June 9, an event sponsored by e-commerce giant Alibaba and China's largest gay dating app, Blued.
Back in Shanghai, it was a sign of progress that there was no local government interference in the seventh ShanghaiPRIDE festival, which concluded on June 21, as in some previous years. I witnessed the first festival in 2009 when some of the events had to be cancelled. A total of 6,000 people participated in this year's festival, which carried the theme of "Love Is Our Future" and included events such as a pride run, bike ride, panel discussions, performances, film screenings and of course, parties.
But still, Chinese officials, at local and central government levels, have not spoken publicly about the rights of gays and lesbians, since homosexuality was decriminalized in 1997 and removed from the list of mental illnesses in 2001.
Hopefully the US Supreme Court decision last Friday will encourage the silent majority, officials and ordinary citizens alike, to take actions to help build a society that shows more tolerance and respect to the LGBT community and upholds their equal rights.
The author is deputy editor of China Daily USA. chenweihua@chinadailyusa.com